For over a decade, mobile money and digital financial services (DFS) have proven to be the main vehicles for improving financial inclusion among the unbanked and underserved citizens in emerging markets. As of December 2019, over 290 mobile money services were live in 95 markets across Africa, Asia, Latin America and the Middle East, with close to USD 2 Billion in daily transactions, consequently unlocking financial access for billions of people.
Mobile money is the most popular financial service in Sub-Saharan Africa. At least half of the 290 mobile money services worldwide are currently live in the continent and in Kenya, mobile money transaction volume constitutes nearly 50% of our GDP.
Mobile money has been instrumental in helping Kenya achieve near-total financial inclusion, currently at 82.9 percent; the highest on the African continent.
As the uptake of mobile money services and e-commerce continues to grow, there has been a widespread integration in broader payment infrastructures, connecting a variety of financial services providers.
Interoperability can be defined as the ability of different systems to connect with one another, exchange and make use of certain information. Interoperability in DFS can be defined as the ability of a digital financial service to make and exchange specific kinds of information often in the form of transactions across a number of financial service providers.
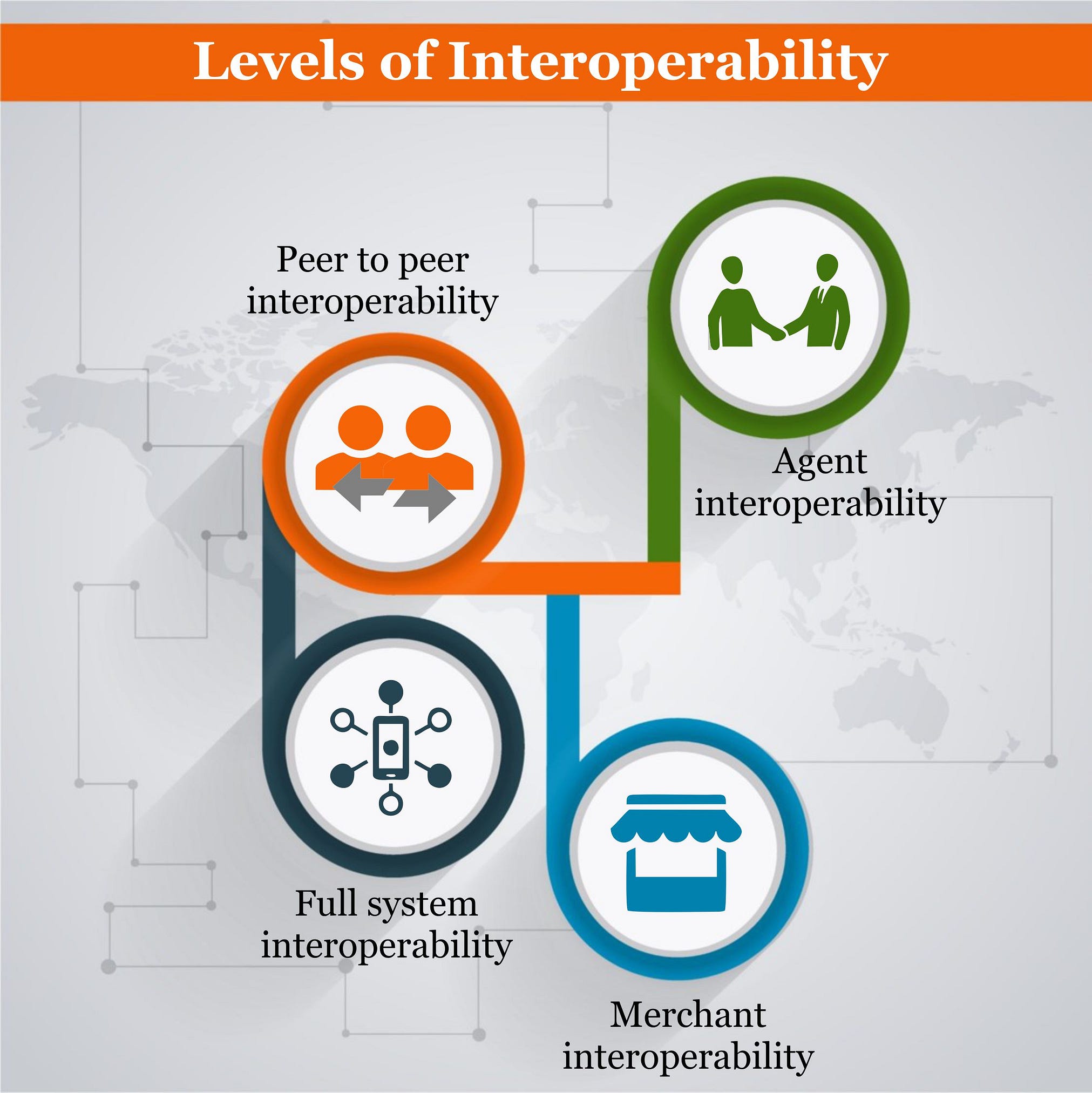
There are many different levels and layers of interoperability in DFS due to the different ways in which it can be achieved. For instance, CGAP breaks down interoperability into three broad types: Bilateral agreements that’s between two providers; multilateral agreements among three or more providers and third-party solutions that link multiple providers. On the other hand, Better Than Cash Alliance defines four different levels of interoperability. They include peer to peer interoperability, merchant interoperability, agent interoperability and full system interoperability. Peer to peer interoperability is where individual institutions connect one on one through individual connections while for agent interoperability, agents operate transactions between multiple providers. Merchant interoperability is defined as where merchants can accept payments from any provider and full systems interoperability refers to financial institutions including banks, microfinance institutions (MFIs) and mobile network operators (MNOs) are all connecting to a common platform, thus enabling transactions.
Benefits of the different types of interoperable mobile money systems affect the entire mobile money ecosystem. Regulators would benefit by having advanced financial inclusion and further formalizing the financial system. End-users on the other hand would have access to a wider variety of financial products and services and would benefit from more efficient systems.
Whilst most regulators and providers have implemented interoperability models in the form of multilateral and bi-lateral agreements to improve efficiency, a lot is still yet to be achieved in leveraging agent interoperability to increase the uptake of financial services.
Executed properly, an interoperable network at the agent level will go a long way in improving long-term financial inclusion by increasing financial and digital services available for consumers and stimulating the circulation of digital values in payment ecosystems. Additionally, increased agent interoperability will offer a range of benefits for end users, from positive socioeconomic outcomes to greater convenience. As such, we believe a lot can be achieved on financial inclusion when mobile money services are interoperable at the agent level.
Our interoperable platform enables mobile money agents and end users to access a variety of financial and digital commerce services thus acting as a means of bringing in more people especially those in underserved areas into the formal financial system, consequently fostering financial inclusion. The PesaKit platform also increases profitability for agents due to the expanded revenue sources. Additionally, PesaKit enables mobile money agents to access an interoperable electronic float when serving customers of different banks and MNOs.
The PesaKit platform strives to improve efficiency at the agent level, further drive financial inclusion for the underserved and nudge Kenya and many other emerging markets towards a more interconnected and inclusive mobile money industry.